A Guide to ESG in Commercial Real Estate
The future of commercial real estate is becoming increasingly tied to Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) considerations. Investors and tenants place greater emphasis on sustainability and social responsibility. In turn, companies are adapting by incorporating ESG principles into their operations.
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) refers to the three key areas that companies and investors consider when evaluating a business. Each pillar within ESG is important to consider when assessing the sustainability and ethical practices of a company.
Fischer Solutions propriety solution, Visual Manager, can help you track and assess the emissions of your real estate portfolio. Lowering the carbon footprint of your operations is the end goal. But first, it is imperative to understand why this is such a hot topic.
The Three Pillars of ESG
One of the key trends in the future of ESG in commercial real estate is the increased demand for sustainable buildings. Tenants are seeking out buildings that are designed to minimize environmental impact and promote health and well-being. This includes features such as energy-efficient lighting, smart building systems, and green roofs.
Considering all three pillars of ESG is important for companies and investors who prioritize sustainability and ethical practices. Each pillar provides unique insights into a company’s impact on the world around it.
| (E) Environmental | (S) Social | (G) Governance | |
| Definition: | Measuring a company’s impact on the environment. | Measuring a company’s impact on society, including its relationship with employees, customers, suppliers, and communities. | Measuring a company’s internal management and decision-making processes. |
| Factors: | Carbon Footprint Energy Usage Waste Management Resource Depletion | Employee Rights Diversity and Inclusion Human Rights Product Safety Community Engagement | Leadership Structure Board Diversity Transparency Ethics |
| Goal: | Reduce negative impact on the environment and promote conservation efforts. | Promote social justice and equality. | Ensure accountability, transparency, and ethical behavior. |
Environmental
The Environmental pillar refers to a company’s impact on the natural environment. Fischer Solutions has the technology to assess the environmental impact of ESG in your commercial real estate portfolio. We can assist with better decision making for the future. More to come on that later in this blog.
Here are some key factors to consider under the Environmental pillar of ESG:
- Climate change: This is one of the primary concerns under the Environmental pillar of ESG. Reduce the carbon footprint by minimizing greenhouse gas emissions, increasing energy efficiency, and transitioning to renewable energy sources.
- Energy usage: Companies may also prioritize sustainable energy practices. Reducing energy usage and promoting the use of renewable energy sources, in order to minimize their impact on the environment.
- Water usage: Reduce water usage and promote water conservation efforts, to minimize impact on the environment.
- Waste management: Reduce waste production and properly manage waste disposal, in order to minimize harm to the environment.
- Resource depletion: Prioritize sustainable practices that reduce impact on natural resources such as forests, minerals, and other non-renewable resources.
- Biodiversity: Protect and promote biodiversity, such as protecting endangered species and habitats, in order to minimize harm to the environment.
Overall, companies that prioritize the Environmental pillar of ESG issues aim to reduce their negative impact on the natural environment. They also promote sustainable practices that preserve natural resources for future generations.
By prioritizing environmental sustainability, companies can establish themselves as responsible and accountable corporate citizens. In turn, this benefits the long-term sustainability and profitability of the business.
Social
The second pillar of ESG refers to a company’s impact on society. This includes various factors such as employee rights, diversity and inclusion, human rights, product safety, and community engagement.
- Employee Rights – promote fair labor practices, such as providing fair wages, benefits, and safe working conditions for employees.
- Diversity and inclusion – promote diversity and inclusivity in hiring practices, as well as within workplace culture.
- Human Rights – ensure that supply chains do not rely on forced or child labor. Also, avoid business practices that contribute to human rights abuses.
- Product safety – ensure that products are safe for consumers and meet ethical standards in terms of production, sourcing, and distribution.
- Community engagement – engage with the communities in which they operate, promoting local economic development and supporting social causes.
Companies that prioritize the social pillar of ESG aim to promote fair and ethical business practices that benefit society as a whole. By prioritizing social sustainability, companies can foster strong relationships with employees, customers, and communities. This will benefit the long-term sustainability and profitability of the business.
Governance
The third pillar of ESG, Governance (G), refers to a company’s internal management and decision-making processes. This includes various factors such as leadership structure, board diversity, transparency, ethics, and risk management.
One of the primary concerns under this pillar is leadership structure. Companies that prioritize governance sustainability aim to have effective and accountable leadership structures. This ensures that the company’s decisions align with the long-term interests of the business and its stakeholders.
Board diversity is another important factor to consider. Aim to have diverse boards of directors. This brings a variety of perspectives and expertise to the company’s decision-making processes.
Transparency is another important issue under this pillar. Prioritizing governance sustainability means transparency about their business practices and decision-making processes, making information readily available to stakeholders.
Companies that prioritize governance sustainability aim to have strong ethical standards, which promote accountability, integrity, and responsible business practices.
Finally, risk management is another important factor under the governance pillar. Effective risk management strategies can help anticipate and mitigate potential risks to the business.
Overall, companies that prioritize the governance pillar of ESG aim to promote responsible and accountable decision-making processes that benefit the long-term interests of the business and its stakeholders. By prioritizing governance sustainability, companies can establish trust and credibility with stakeholders. They also identify risks and opportunities to aid with their investment decisions.
Understanding the Consequences
The consequences of not meeting ESG requirements can vary depending on the specific requirements and the context. Here are some potential consequences that businesses may face for failing to meet ESG requirements:
- Reputational damage: Failing to meet ESG requirements can damage a business’s reputation. This can lead to loss of customers, difficulty attracting new investors or tenants, and other negative impacts on the business.
- Legal and regulatory penalties: Businesses may face legal or regulatory penalties for failing to comply, depending on the ESG factors in question.
- Financial penalties: In some cases, failing to meet ESG requirements can result in financial penalties. Higher insurance premiums, increased borrowing costs, or reduced access to capital are a few examples.
- Reduced access to capital: Investors and lenders are increasingly factoring ESG in commercial real estate considerations into their decision-making processes. Businesses that fail to meet ESG requirements may find it more difficult to access capital or secure favorable financing terms.
- Increased risk: Failing to meet ESG requirements can increase a business’s exposure to risk. This can lead to financial losses, legal liabilities, and other negative impacts on the business.
Overall, failing to meet ESG requirements can have significant negative consequences for businesses. As a result, it is increasingly important for businesses to take ESG considerations seriously. Proactively manage ESG performance in order to mitigate these risks and secure long-term success.
Tracking the E in ESG
The integration of technology to help monitor and improve the performance of ESG in commercial real estate is where Fischer Solutions comes into the equation. Companies are adopting technologies such as sensors and data analytics to track energy usage, water consumption, and waste generation. Fischer Solutions can aggregate that data as part of our asset management software.
ESG data can be used to identify areas for improvement and to benchmark performance against industry standards. Not only is health and safety important, but corporate governance needs to be reviewed when a company is ESG investing.
The Scopes of Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions
The GHG scopes are a set of categories used to define and measure the greenhouse gas emissions of an organization. The GHG Protocol, which is the most widely used international accounting tool for GHG emissions, identifies three scopes of emissions:
1. Scope 1 emissions: These are direct emissions from sources that are owned or controlled by the organization. Examples include:
- emissions from the combustion of fuel in boilers or furnaces
- emissions from on-site transportation
- emissions from chemical reactions during production processes
2. Scope 2 emissions: These are indirect emissions from the consumption of purchased electricity, heat, or steam. They are generated from the production of energy off-site. These are associated with the consumption of that energy by the organization.
3. Scope 3 emissions: These are all other indirect emissions that occur in the value chain of the organization. This includes emissions from:
- the extraction and production of purchased materials
- transportation and distribution of products
- use of products
- disposal of waste generated by the organization
The scopes are important because they help organizations identify the sources of their GHG emissions. This leads to the development of strategies to reduce their environmental impact. Organizations can demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and reduce their environmental impact.
Ways to Track ESG in Commercial Real Estate
There are a variety of software solutions available to help businesses track their ESG performance for real estate assets. Here are some types of software that businesses may consider:
- ESG management platforms: These are software solutions that are designed specifically to help businesses track and manage their ESG performance across various asset types, including real estate. These platforms may include features such as data tracking and reporting, risk assessment, stakeholder engagement, and benchmarking against industry standards.
- Energy management software: Businesses may also use energy management software to track and manage the energy consumption of their real estate assets. These solutions may include features such as real-time energy monitoring, data analytics, and automated reporting.
- Building automation systems: Building automation systems (BAS) are software solutions that help businesses control and manage the various building systems in their real estate assets, such as heating, ventilation, air conditioning (HVAC), lighting, and security. These systems can help businesses optimize energy usage, reduce waste, and improve the overall sustainability of their buildings.
- Data analytics platforms: Businesses may also use data analytics platforms to track and analyze data related to their real estate assets’ ESG performance. These platforms can help businesses identify trends, track progress toward sustainability goals, and make data-driven decisions.
- Sustainability reporting software: Finally, businesses may use sustainability reporting software to help them generate ESG reports for their real estate assets. These solutions can help businesses collect and analyze data, generate reports, and communicate their sustainability performance to stakeholders.
Overall, the specific software solutions that businesses choose will depend on their unique needs and requirements. However, by leveraging the right software tools, businesses can more effectively track and manage their ESG performance for their real estate assets. This helps to improve sustainability, reduce costs, and attract and retain tenants and investors over the long term.
Visual Manager and GHG Emissions
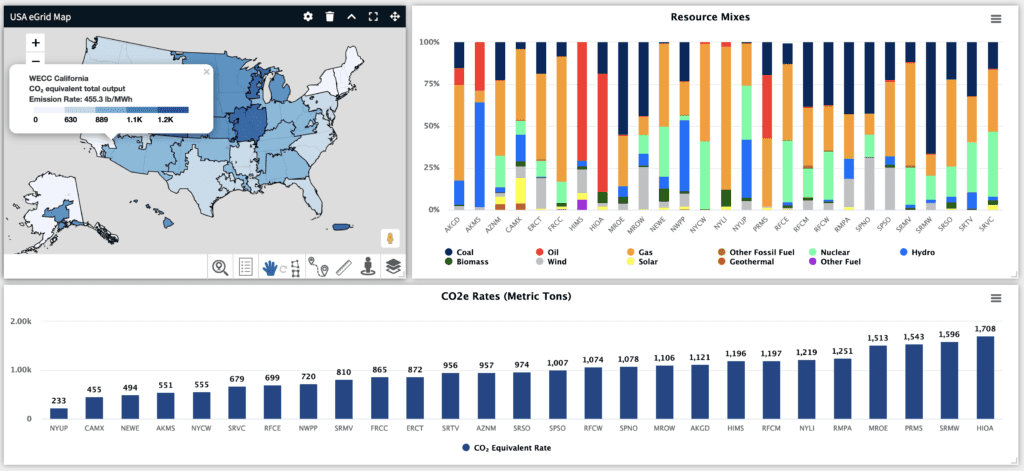
As part of Fischer Solutions’ mission to provide an end-to-end real estate lifecycle management system, our technology supports ESG information. GHG and carbon emissions can be tracked through public databases and integrated into your property data through Visual Manager.
What is Visual Manager?
Visual Manager is the premier corporate real estate business intelligence reporting and analysis solution. It is the perfect platform to analyze and report your Scope 1 and Scope 2 GHG emissions. It also tracks water consumption at the property level and helps you understand how your real estate portfolio is impacting your emissions.
This reporting allows robust data auditing, and granular reporting in a company’s business hierarchy. By enabling spatial and asset-type reporting, it allows companies to compare their portfolios to benchmarks and quickly identify outliers in their energy consumption. This exposes inefficient buildings for further analysis to potentially:
- establish more efficient processes
- target for relocation
- work with the landlord to make significant investments in efficiencies
It also lets you measure the ROI of investment programs or operational improvements. For example, LED re-fittings and other building modernization efforts or automatically turning the lights off at night/ on weekends.
What Can Visual Manager Do for Tracking GHG Emissions?
Visual Manager can report on and analyze anything. Our differentiator is knowing how to provide value from the ESG data that is relevant to our Corporate Real Estate Clients.
For our clients, it’s about delivering robust and elegant reporting that withstands scrutiny, is easily auditable, and opens new ways to navigate their data to reach insights.
We enable our CRE Clients to track their GHG and Carbon emissions of leased or owned assets such as:
- Real Estate
- Equipment
- Fleet
Visual Manager uses data and calculations configured by the GHG Emissions Protocol and EPA Energy grid emissions factors.
But that’s not all. We also have the ability to track and analyze additional environmental factors such as:
- Energy Consumption
- Water Usage
- Waste Management
- Resource Depletion
Data can be collected from multiple sources to provide the exact analysis that a company might need when making decisions for their leased and owned assets. As ESG reporting continues to evolve, Visual Manager will be able to grow in sync to provide the most up-to-date data necessary for building a sustainable future.
Visual Manager in Action
Utility Data, both financial and consumption data, is tracked in either ManagePath or a third-party solution. Companies pay for solutions that take in utility invoices automatically and abstract the pricing and consumption data to potentially generate the payments for the utilities.
The abstracted utility data can be sent to Visual Manager to analyze in combination with the property database. Reporting in Visual Manager has allowed our clients to identify auto-abstracted errors and correct them in their base system.
The combining of the utility data with the property data is a major enhancement for reporting, analysis, and investment. This gives stakeholders a more well-rounded grasp on the value and the impact of ESG in Commercial Real Estate, and how they can work to achieve sustainability within their portfolio.
Conclusion
Overall, the future of commercial real estate is increasingly focused on ESG considerations. Companies that are able to adapt to these trends and incorporate sustainability and social responsibility into their operations will be well-positioned to succeed in the years ahead. Fischer Solutions is the missing piece of your ESG puzzle! Request a demo today to see how we can help you prepare your real estate portfolio for a sustainable future!
